Select all of the true statements about hydrocarbon structure embarks on an enthralling journey into the realm of hydrocarbons, exploring their fundamental structure, bonding characteristics, molecular shapes, and chemical reactivity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these organic compounds, providing a thorough understanding of their properties and behavior.
From the fundamental building blocks of carbon-hydrogen bonds to the complex interplay of functional groups, this narrative unravels the secrets of hydrocarbon structure, revealing the intricate relationship between their molecular architecture and their diverse applications.
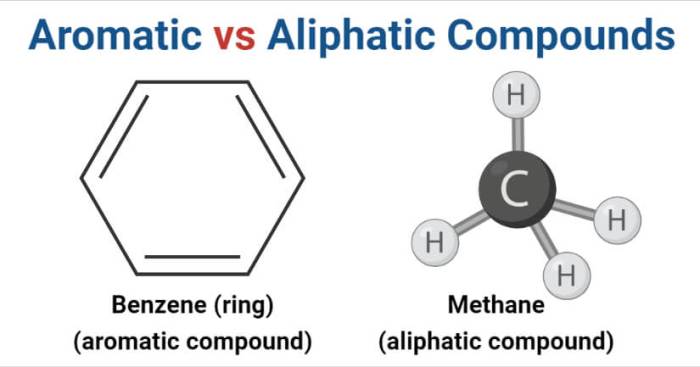
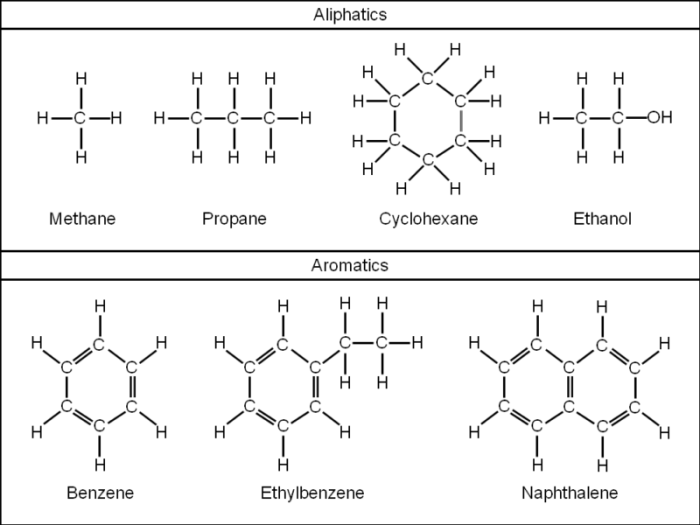
Hydrocarbon Structure Basics: Select All Of The True Statements About Hydrocarbon Structure
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed solely of hydrogen and carbon atoms. Their structure plays a crucial role in determining their physical and chemical properties.
Carbon-Hydrogen Bonds and Molecular Geometry
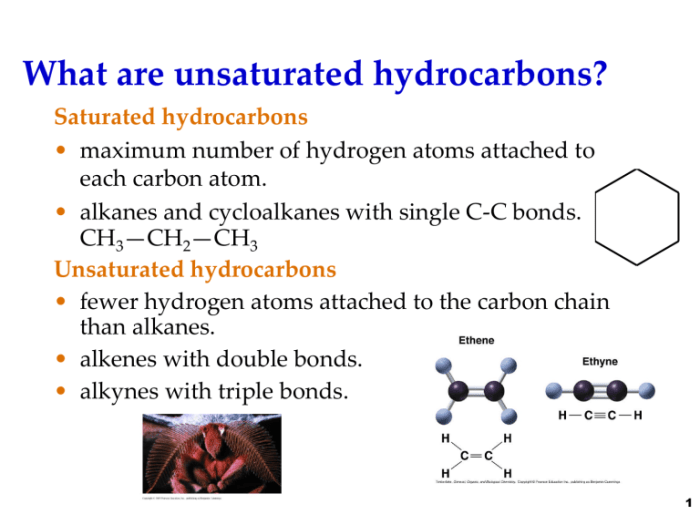
In hydrocarbons, carbon atoms form covalent bonds with hydrogen atoms through shared electron pairs. The hybridization of carbon atoms determines the molecular geometry of hydrocarbons. Alkanes, with tetrahedral carbon atoms, have a linear or branched structure. Alkenes, with trigonal planar carbon atoms, have a double bond between carbon atoms, resulting in a bent shape.
Alkynes, with linear carbon atoms, have a triple bond between carbon atoms, giving them a linear shape.
Bonding and Hybridization, Select all of the true statements about hydrocarbon structure
Carbon atoms in hydrocarbons undergo hybridization, which involves the mixing of atomic orbitals to form hybrid orbitals. In alkanes, sp 3hybridization occurs, resulting in four equivalent hybrid orbitals that form tetrahedral bonds with hydrogen atoms. In alkenes, sp 2hybridization occurs, forming three equivalent hybrid orbitals that form trigonal planar bonds with other carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms.
In alkynes, sp hybridization occurs, resulting in two equivalent hybrid orbitals that form linear bonds with other carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms.
FAQ Resource
What are the fundamental building blocks of hydrocarbons?
Carbon-hydrogen bonds
How does hybridization affect the bonding properties of hydrocarbons?
It determines the geometry and strength of the bonds formed by carbon atoms.
What is the relationship between hydrocarbon structure and molecular shape?
The arrangement of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms dictates the overall molecular shape, which can be linear, branched, or cyclic.