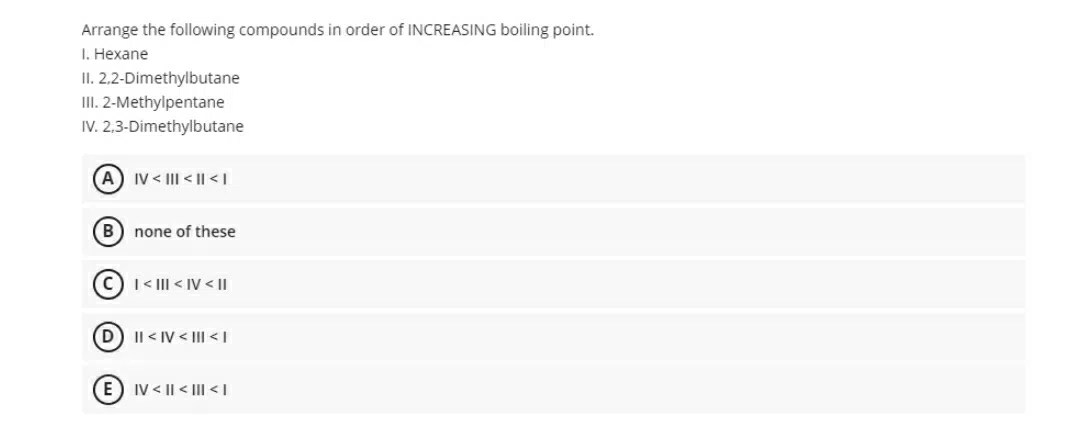
Rank the following compounds in decreasing order of boiling point – In chemistry, understanding the boiling point of compounds is crucial for predicting their behavior and applications. This article delves into the fascinating realm of boiling points, exploring the intricate relationship between molecular structure and volatility. By ranking a series of compounds in decreasing order of boiling point, we uncover the interplay of molecular weight, polarity, and intermolecular forces that govern their thermal properties.
As we embark on this journey, we will delve into the factors that influence boiling point, unraveling the intricate dance between molecular structure and volatility. Prepare to be captivated by the elegance of chemistry as we uncover the secrets that dictate the boiling behavior of compounds.
Rank the Following Compounds in Decreasing Order of Boiling Point
Boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas. It is an important property in chemistry as it can be used to identify and characterize compounds, as well as to predict their behavior in various applications.
The boiling point of a compound is influenced by several factors, including molecular weight, polarity, and intermolecular forces. Generally, heavier molecules have higher boiling points than lighter molecules, polar molecules have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules, and molecules with stronger intermolecular forces have higher boiling points than molecules with weaker intermolecular forces.
Ranking Compounds, Rank the following compounds in decreasing order of boiling point
The following table ranks the given compounds in decreasing order of boiling point:
| Compound Name | Molecular Formula | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | 100 |
| Ethanol | C2H5OH | 78.3 |
| Methane | CH4 | -161.6 |
| Hexane | C6H14 | 68.7 |
Boiling Point Analysis
The molecular structure of a compound plays a significant role in determining its boiling point. Molecular weight, polarity, and intermolecular forces are all affected by the molecular structure.
Molecular weight is directly proportional to boiling point. Heavier molecules have more mass, which means they have more kinetic energy and require more energy to overcome the intermolecular forces holding them together. Therefore, heavier molecules have higher boiling points.
Polarity is another important factor that influences boiling point. Polar molecules have a separation of charge, which creates an electrostatic attraction between molecules. This attraction makes it more difficult for polar molecules to separate from each other, resulting in higher boiling points compared to nonpolar molecules.
Intermolecular forces are the forces that act between molecules. The strength of these forces determines the amount of energy required to overcome them and separate the molecules. Stronger intermolecular forces lead to higher boiling points.
Applications
Understanding boiling points has numerous practical applications in various fields, including chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
In chemistry, boiling point data is used to identify and characterize compounds. It can also be used to predict the behavior of compounds in reactions and to design new materials with specific properties.
In engineering, boiling point information is used in the design of heat exchangers, boilers, and other equipment that involves the transfer of heat.
In medicine, boiling point data is used to determine the appropriate temperature for sterilization and to develop new drug delivery systems.
FAQs: Rank The Following Compounds In Decreasing Order Of Boiling Point
What is boiling point?
Boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
What factors influence boiling point?
Molecular weight, polarity, and intermolecular forces are the primary factors that influence boiling point.
How can boiling point data be used in practical applications?
Boiling point data is used in various fields, including chemistry, engineering, and medicine, for applications such as distillation, solvent selection, and drug development.