Delving into the realm of economics, we present production possibilities frontier worksheet answers, an invaluable resource for comprehending the fundamental concepts of production and opportunity cost. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of the production possibilities frontier (PPF), empowering you with the knowledge to navigate economic decision-making with precision.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the theoretical underpinnings of the PPF, its graphical representation, and the underlying assumptions and limitations. Through step-by-step guidance, we will equip you with the skills to tackle PPF worksheet questions with confidence.
Furthermore, we will uncover the practical applications of PPF analysis in real-world decision-making, showcasing its relevance in shaping economic policies and fostering economic growth.
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) Concept
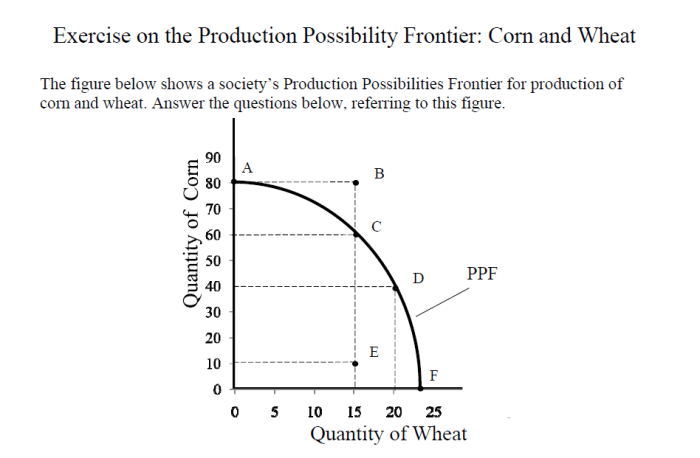
A production possibilities frontier (PPF) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
The PPF assumes that the economy is operating at full employment and that resources are fully utilized. It also assumes that technology is fixed and that there are no external factors influencing production.
Assumptions and Limitations of a PPF, Production possibilities frontier worksheet answers
- Full employment:The PPF assumes that all available resources are being used to produce goods and services.
- Fixed technology:The PPF assumes that the technology used to produce goods and services is fixed.
- No external factors:The PPF assumes that there are no external factors, such as natural disasters or changes in consumer demand, that can affect production.
PPF Worksheet Answers
To answer PPF worksheet questions, follow these steps:
- Identify the two goods or services that are being produced.
- Plot the points that represent the maximum possible combinations of the two goods or services.
- Connect the points with a line to create the PPF.
- Answer the questions on the worksheet using the PPF.
Here is an example of a PPF worksheet question:
What is the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of Good X?
To answer this question, find the point on the PPF that represents the production of one more unit of Good X. Then, move along the PPF to the point that represents the same production of Good Y. The difference in the production of Good Y is the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of Good X.
Applications of PPF Analysis
PPF analysis can be used to make decisions about how to allocate resources. For example, a government can use PPF analysis to decide how to allocate its budget between different programs.
PPF analysis can also be used to compare the production capabilities of different countries. For example, a country with a more advanced technology will have a PPF that is shifted outward compared to a country with a less advanced technology.
Factors Affecting PPF
There are a number of factors that can shift a PPF. These factors include:
- Technology:Advances in technology can shift the PPF outward, allowing an economy to produce more of both goods and services.
- Resources:An increase in resources, such as labor or capital, can shift the PPF outward.
- Consumer demand:Changes in consumer demand can shift the PPF. For example, an increase in demand for Good X will shift the PPF outward in the direction of Good X.
PPF and Economic Growth
Economic growth is the increase in the production of goods and services over time. PPF analysis can be used to show how economic growth can lead to an expansion of the PPF.
There are two main ways that economic growth can lead to an expansion of the PPF:
- Technological advancements:Technological advancements can lead to an expansion of the PPF by allowing an economy to produce more of both goods and services with the same resources.
- Increased resources:An increase in resources, such as labor or capital, can also lead to an expansion of the PPF.
Comparative Advantage and PPF
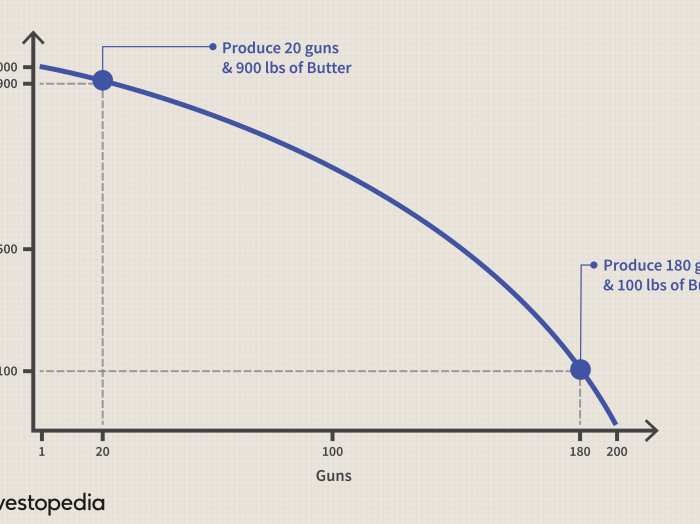
Comparative advantage is the ability of a country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country.
PPF analysis can be used to show how countries can benefit from specializing in the production of goods and services where they have a comparative advantage.
For example, suppose that Country A has a comparative advantage in the production of wheat and Country B has a comparative advantage in the production of cloth.
If Country A and Country B both specialize in the production of the good in which they have a comparative advantage, they can both produce more of both goods than if they tried to produce both goods themselves.
PPF and Opportunity Cost: Production Possibilities Frontier Worksheet Answers
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is given up when a decision is made.
PPF analysis can be used to show how opportunity cost is reflected in the production of goods and services.
For example, the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of Good X is the amount of Good Y that must be given up.
Policy Implications of PPF Analysis
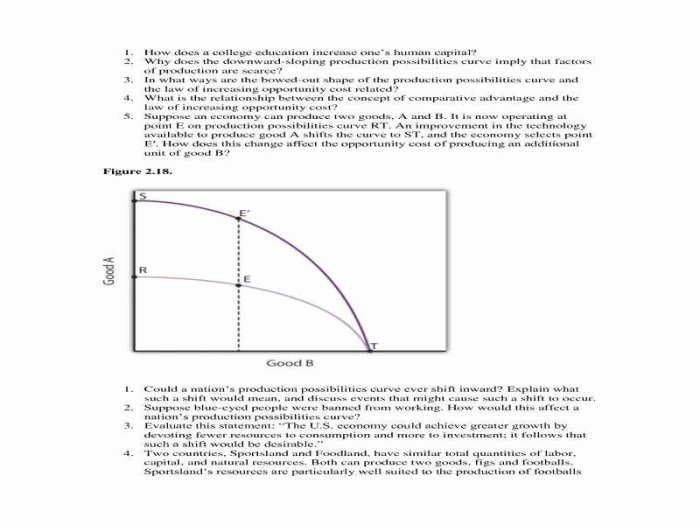
PPF analysis can be used to inform economic policy decisions.
For example, a government can use PPF analysis to:
- Allocate resources efficiently:PPF analysis can be used to help a government allocate resources efficiently between different programs.
- Promote economic growth:PPF analysis can be used to help a government promote economic growth by identifying policies that will lead to an expansion of the PPF.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the production possibilities frontier (PPF)?
The production possibilities frontier (PPF) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
What is opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is foregone when a choice is made.
How can PPF analysis be used in decision-making?
PPF analysis can be used to help decision-makers understand the trade-offs involved in producing different combinations of goods and services.
What are the factors that can shift a PPF?
The factors that can shift a PPF include changes in technology, changes in the availability of resources, and changes in consumer preferences.
