Embark on a journey to uncover the intricacies of que es el intercambio colombino, an era marked by a profound exchange of ideas, goods, and cultures that reshaped the world. From the introduction of new crops to the spread of diseases, the Columbian Exchange left an indelible mark on human history, and its legacy continues to resonate today.
Delve into the historical context that set the stage for this momentous exchange, tracing the key events and their significance. Explore the biological impacts, including the introduction of new species and the resulting ecological transformations. Uncover the cultural exchanges that facilitated the diffusion of ideas, technologies, and customs, and examine the role of explorers, missionaries, and traders in this process.
Historical Context
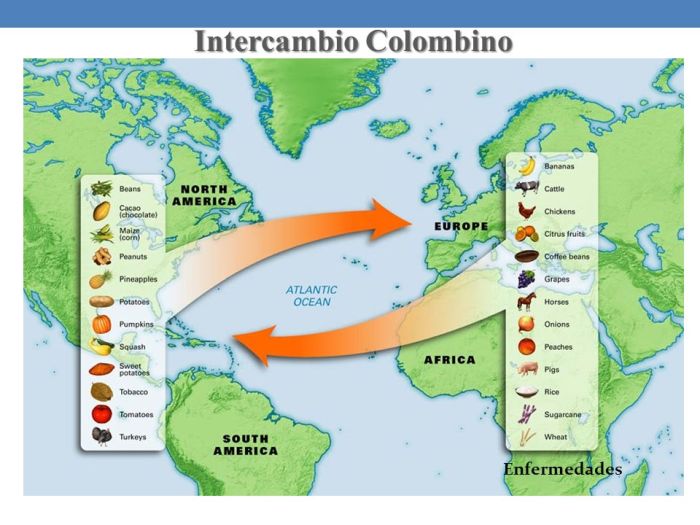
The Columbian Exchange was a period of cultural and biological exchange between the Americas, Europe, and Africa that began with Christopher Columbus’s arrival in the Americas in 1492. This exchange had a profound impact on all three continents, leading to the introduction of new crops, animals, and diseases.
The Columbian Exchange can be divided into two main phases. The first phase, from 1492 to 1600, was characterized by the introduction of European plants and animals to the Americas and the exchange of American crops and animals to Europe.
The second phase, from 1600 to 1800, saw the introduction of African slaves to the Americas and the spread of European diseases to Africa.
Key Events and Their Significance
- 1492:Christopher Columbus arrives in the Americas, marking the beginning of the Columbian Exchange.
- 1519:Hernán Cortés lands in Mexico, leading to the conquest of the Aztec Empire.
- 1532:Francisco Pizarro lands in Peru, leading to the conquest of the Inca Empire.
- 1619:The first African slaves are brought to the Americas.
- 1796:Edward Jenner develops the smallpox vaccine, which helps to control the spread of smallpox in the Americas.
Biological Impacts
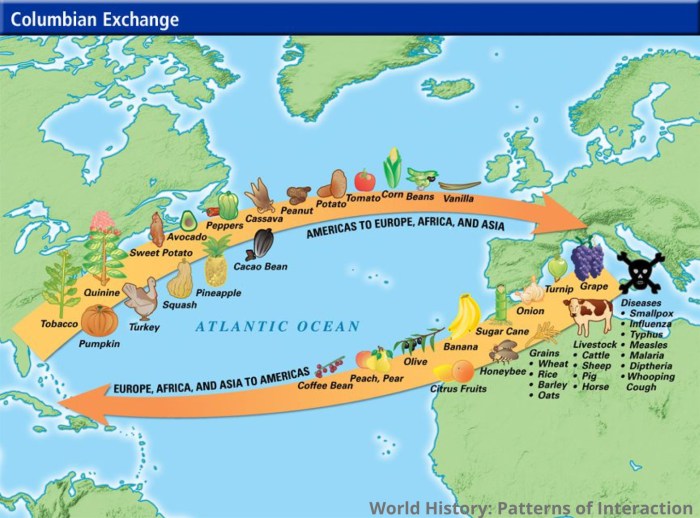
The Columbian Exchange profoundly altered the biological landscapes of both the Americas and Europe. The introduction of new crops, livestock, and diseases had far-reaching consequences for the indigenous populations.
Introduction of New Crops
One of the most significant impacts of the Columbian Exchange was the introduction of new crops to the Americas. These included maize (corn), potatoes, tomatoes, beans, and squash. These crops became staple foods for many indigenous populations and played a vital role in their survival and prosperity.
Introduction of Livestock
In addition to new crops, the Columbian Exchange also introduced livestock to the Americas. These included horses, cattle, pigs, and sheep. These animals provided a new source of food and transportation for indigenous populations and played a key role in their economic development.
Impact on Indigenous Populations
The introduction of new crops and livestock had a profound impact on indigenous populations. In some cases, these introductions led to increased food production and economic growth. In other cases, they led to environmental degradation and the displacement of indigenous peoples.
Species that Thrived
- Maize (corn): Became a staple food for many indigenous populations in the Americas.
- Potatoes: Thrived in the Andean region of South America and became a major source of nutrition for indigenous peoples.
- Horses: Provided a new mode of transportation for indigenous peoples and played a key role in their hunting and warfare.
Species that Declined
- Native American bison: The introduction of horses led to a decline in bison populations due to increased hunting.
- Passenger pigeons: The introduction of European diseases led to a decline in passenger pigeon populations.
- Chestnut trees: The introduction of chestnut blight from Asia led to the decline of chestnut trees in North America.
Cultural Exchange
The Columbian Exchange witnessed a profound exchange of cultural practices, ideas, and technologies between the Americas, Europe, and Africa. This exchange had a transformative impact on the societies involved, shaping their cultural landscapes in various ways.
The diffusion of ideas and technologies was facilitated by explorers, missionaries, and traders. Explorers brought back accounts of new lands and their inhabitants, while missionaries spread religious beliefs and practices. Traders introduced new crops, livestock, and manufacturing techniques.
Diffusion of Ideas and Beliefs, Que es el intercambio colombino
The Columbian Exchange introduced new religious ideas to the Americas. Spanish missionaries brought Catholicism, which became the dominant religion in much of Latin America. In Africa, European missionaries introduced Christianity and Islam, which gained followers in various regions.
Adoption of New Technologies
The exchange of technologies had a significant impact on the economies and lifestyles of the involved societies. The Americas received horses, cattle, pigs, and sheep, which transformed agriculture and transportation. Europe gained access to new crops such as maize, potatoes, and tomatoes, which became staples in European diets.
El intercambio colombino, un acontecimiento histórico que transformó el mundo, es un tema fascinante que sigue inspirando hoy en día. En este sentido, la convención estatal de la FFA de Wisconsin de 2023 abordará el impacto del intercambio colombino en la agricultura y la educación.
Al explorar las conexiones entre el pasado y el presente, podemos obtener valiosos conocimientos que nos ayuden a comprender mejor el intercambio colombino y su relevancia continua.
Cultural Assimilation and Syncretism
In some cases, cultural exchange led to the assimilation of new practices into existing cultures. For example, in Latin America, indigenous beliefs and practices blended with Catholicism, creating a unique syncretic religious tradition.
Economic Consequences: Que Es El Intercambio Colombino
The Columbian Exchange had significant economic implications, reshaping global trade and commerce. The introduction of new crops, livestock, and resources led to the establishment of new trade routes and the rise of mercantilism.
New Trade Routes and Global Commerce
The Columbian Exchange opened up new trade routes between the Americas, Europe, Africa, and Asia. These routes facilitated the exchange of goods such as spices, sugar, tobacco, and precious metals. The increased trade volume stimulated economic growth and led to the rise of commercial centers like Lisbon, Seville, and Antwerp.
Resource Exploitation and Mercantilism
The discovery of vast natural resources in the Americas, such as gold, silver, and timber, led to a surge in resource exploitation. European powers established colonies and exploited these resources to fuel their economies. This exploitation led to the rise of mercantilism, an economic system that emphasized the accumulation of wealth through trade and the acquisition of colonies.
Disease and Population Changes
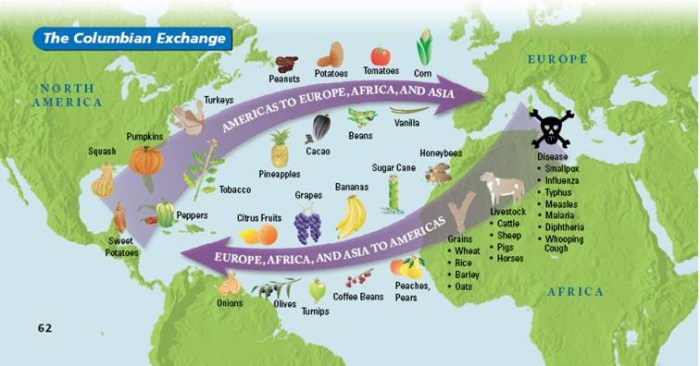
The Columbian Exchange not only introduced new crops and livestock but also brought devastating diseases to both hemispheres. The spread of diseases had a profound impact on indigenous populations, leading to significant demographic shifts.
Impact on Indigenous Populations
European colonizers brought with them diseases such as smallpox, measles, and influenza, which were new to the indigenous populations of the Americas. These diseases spread rapidly through the indigenous communities, decimating their populations. It is estimated that up to 90% of the indigenous population in the Americas died from European diseases within a century of contact.
Role of Immunity and Quarantine Measures
The indigenous populations had no immunity to these diseases, making them highly susceptible to infection. Moreover, their lack of access to healthcare and sanitation measures further exacerbated the spread of disease. In contrast, European colonizers had developed some immunity to these diseases over centuries of exposure.
They also implemented quarantine measures to prevent the spread of disease among their own ranks.These factors contributed to the devastating impact of disease on indigenous populations, leading to a sharp decline in their numbers and a significant shift in the demographics of the Americas.
Environmental Impacts

The Columbian Exchange profoundly altered the environments of both the Americas and Europe. The introduction of new species, deforestation, and land use changes had significant consequences for ecosystems and the global climate.
Invasive Species
The Columbian Exchange introduced numerous invasive species to new environments. For example, European rats and mice, brought to the Americas on ships, decimated native bird populations and spread diseases. Similarly, the introduction of Eurasian grasses to the Americas transformed prairies and savannas, altering fire regimes and biodiversity.
Deforestation and Land Use Changes
The arrival of Europeans in the Americas led to widespread deforestation and land use changes. Forests were cleared for agriculture, settlements, and logging, disrupting habitats and altering local climates. The loss of trees contributed to soil erosion, water pollution, and the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Q&A
What is the significance of the Columbian Exchange?
The Columbian Exchange was a period of extensive exchange of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe, which had a profound impact on both continents.
How did the Columbian Exchange affect indigenous populations?
The introduction of European diseases to the Americas had a devastating impact on indigenous populations, leading to widespread mortality and population decline.
What were the economic consequences of the Columbian Exchange?
The Columbian Exchange led to the establishment of new trade routes and the rise of mercantilism, which had a significant impact on global commerce.